HandlerMapping组件 HandlerMapping 组件,请求的处理器匹配器,负责为请求找到合适的 HandlerExecutionChain 处理器执行链,包含处理器(handler)和拦截器们(interceptors)
handler 处理器是 Object 类型,可以将其理解成 HandlerMethod 对象(例如我们使用最多的 @RequestMapping 注解所标注的方法会解析成该对象),包含了方法的所有信息,通过该对象能够执行该方法HandlerInterceptor 拦截器对处理请求进行增强处理,可用于在执行方法前、成功执行方法后、处理完成后进行一些逻辑处理HandlerMapping 组件 回顾一下doDispatch中的调用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 protected void doDispatch (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null ; mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null ) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return ; } } @Nullable protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this .handlerMappings != null ) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this .handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null ) { return handler; } } } return null ; }
注意 ,这里是通过一个一个的 HandlerMapping 组件去进行处理,如果找到对应 HandlerExecutionChain 对象则直接返回,不会继续下去,所以初始化的 HandlerMapping 组件是有一定的先后顺序的,默认是BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping -> RequestMappingHandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 接口 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping 接口,请求的处理器匹配器,负责为请求找到合适的 HandlerExecutionChain 处理器执行链,包含处理器(handler)和拦截器们(interceptors),代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public interface HandlerMapping { String BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingHandler" ; String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping" ; String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern" ; String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping" ; String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables" ; String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables" ; String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes" ; @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain getHandler (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception; }
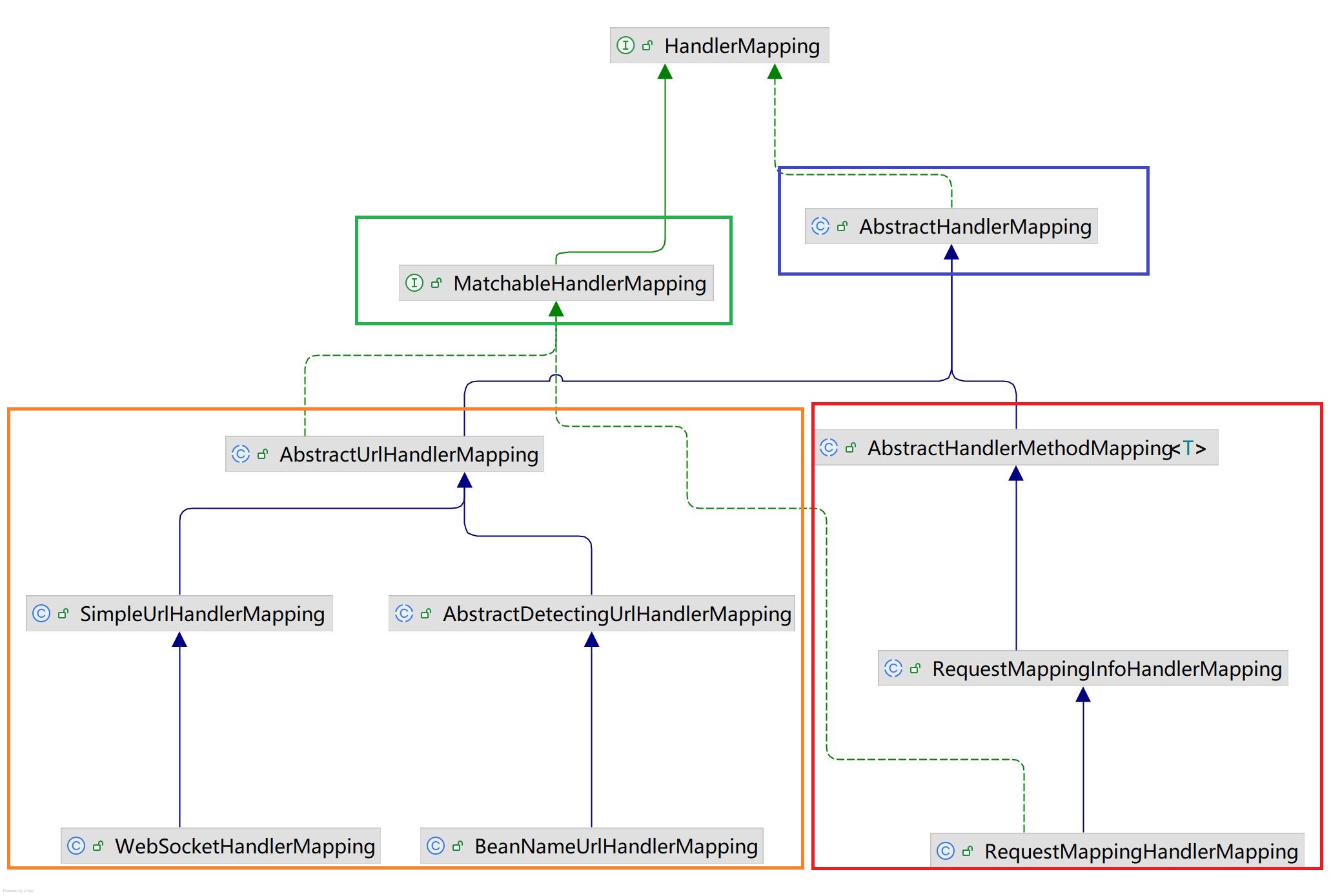
先来看一下继承图
蓝色框 AbstractHandlerMapping 抽象类,实现了 “为请求找到合适的 HandlerExecutionChain 处理器执行链” 对应的的骨架逻辑,而暴露 getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) 抽象方法,交由子类实现
AbstractHandlerMapping 的子类,分成两派,分别是
橙色框 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 系,基于 URL 进行匹配。例如基于xml配置的。当然,目前这种方式已经基本不用了,被 @RequestMapping 等注解的方式所取代。不过,Spring MVC 内置的一些路径匹配,还是使用这种方式。
红色框 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 系,基于 Method 进行匹配 。例如,我们所熟知的 @RequestMapping 等注解的方式。
绿色框的 MatchableHandlerMapping 接口,定义了 “判断请求和指定 pattern 路径是否匹配” 的方法。
初始化过程 在 DispatcherServlet 的 initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) 方法,会在 onRefresh 方法被调用,初始化 HandlerMapping 组件,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 private void initHandlerMappings (ApplicationContext context) { this .handlerMappings = null ; if (this .detectAllHandlerMappings) { Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true , false ); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this .handlerMappings = new ArrayList <>(matchingBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this .handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this .handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { } } if (this .handlerMappings == null ) { this .handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties" ); } } }
如果“开启”探测功能,则扫描已注册的 HandlerMapping 的 Bean 们,添加到 handlerMappings 中,默认开启
如果“关闭”探测功能,则获得 Bean 名称为 “handlerMapping” 对应的 Bean ,将其添加至 handlerMappings
如果未获得到,则获得默认配置的 HandlerMapping 类,调用 getDefaultStrategies() 方法,就是从 DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中读取 HandlerMapping 的默认实现类,如下:1 2 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping =org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping
AbstractHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping,实现 HandlerMapping、Ordered、BeanNameAware 接口,继承 WebApplicationObjectSupport 抽象类
MatchableHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.MatchableHandlerMapping,定义了“判断请求和指定 pattern 路径是否匹配”的方法。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public interface MatchableHandlerMapping extends HandlerMapping { @Nullable RequestMatchResult match (HttpServletRequest request, String pattern) ; }
目前实现 MatchableHandlerMapping 接口的类,有 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类和 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 抽象类,在后续都会进行分析
HandlerInterceptor拦截器 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor,处理器拦截器接口,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public interface HandlerInterceptor { default boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return true ; } default void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } default void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception { } }
HandlerExecutionChain org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain,处理器执行链,也就是通过 HandlerMapping 组件为请求找到的处理对象 ,包含处理器(handler)和拦截器们(interceptors)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class HandlerExecutionChain { private final Object handler; @Nullable private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors; @Nullable private List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList; private int interceptorIndex = -1 ; public HandlerExecutionChain (Object handler) { this (handler, (HandlerInterceptor[]) null ); } public HandlerExecutionChain (Object handler, @Nullable HandlerInterceptor... interceptors) { if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) { HandlerExecutionChain originalChain = (HandlerExecutionChain) handler; this .handler = originalChain.getHandler(); this .interceptorList = new ArrayList <>(); CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(originalChain.getInterceptors(), this .interceptorList); CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, this .interceptorList); } else { this .handler = handler; this .interceptors = interceptors; } } }
handler:请求对应的处理器对象,可以先理解为 HandlerMethod 对象(例如我们常用的 @RequestMapping 注解对应的方法会解析成该对象),也就是我们的某个 Method 的所有信息,可以被执行
interceptors:请求匹配的拦截器数组
interceptorList:请求匹配的拦截器集合,这个属性似乎跟上面一个数组属性是重复的,这里笔者只能猜测可能要实现的逻辑:interceptorList是内部持有的,并没有直接暴露给外部;而interceptors通过getInterceptors方法可以暴露给外部。通过interceptorList向数组array转换的时候,提供了一些便捷?这部分代码是上古的代码,从03年就存在了🤪
interceptorIndex:记录已成功执行前置处理的拦截器位置,因为已完成处理只会执行前置处理成功的拦截器,且倒序执行
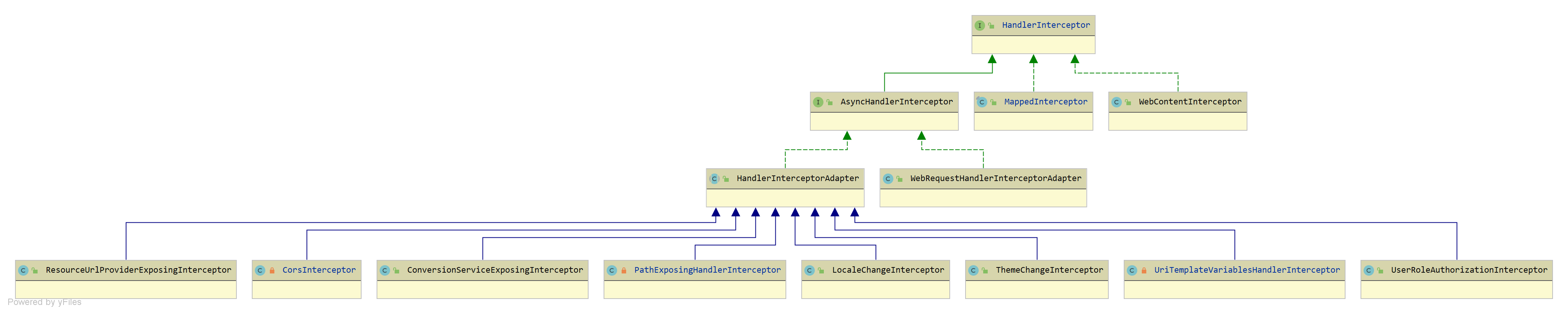
HandlerInterceptor 的实现类 看一下继承图:
MappedInterceptor org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.MappedInterceptor,实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,支持地址匹配的 HandlerInterceptor 实现类<mvc:interceptor />
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <mvc:interceptors > <mvc:interceptor > <mvc:mapping path ="/**" /> <mvc:exclude-mapping path ="/error/**" /> <bean class ="cc.nimbusk.javaweb.interceptor.JwtInterceptor" /> </mvc:interceptor > </mvc:interceptors >
每一个 <mvc:interceptor /> 标签,将被解析成一个 MappedInterceptor 类型的 Bean 拦截器对象
然后 MappedInterceptor 类型的拦截器在 AbstractHandlerMapping 的 initApplicationContext() -> detectMappedInterceptors 会被扫描到1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected void detectMappedInterceptors (List<HandlerInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) { mappedInterceptors.addAll(BeanFactoryUtils .beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true , false ) .values()); }
也就是说在初始化 HandlerMapping 组件的时候会扫描到我们自定义的拦截器,并添加到属性中 。
如何配置interceptor 这里有个问题:<mvc:interceptor /> 标签如何被解析成MappedInterceptor对象的?
1 http\://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc =org.springframework.web.servlet.config.MvcNamespaceHandler
指定了 NamespaceHandler 为 MvcNamespaceHandler 对象,也就是说<mvc />标签会被该对象进行解析 ,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class MvcNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { @Override public void init () { registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven" , new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("default-servlet-handler" , new DefaultServletHandlerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("interceptors" , new InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("resources" , new ResourcesBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-controller" , new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("redirect-view-controller" , new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("status-controller" , new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-resolvers" , new ViewResolversBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("tiles-configurer" , new TilesConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("freemarker-configurer" , new FreeMarkerConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("groovy-configurer" , new GroovyMarkupConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("script-template-configurer" , new ScriptTemplateConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser ()); registerBeanDefinitionParser("cors" , new CorsBeanDefinitionParser ()); } }
其中<mvc:interceptor />标签则会被 InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser 对象进行解析,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser { @Override @Nullable public BeanDefinition parse (Element element, ParserContext context) { context.pushContainingComponent( new CompositeComponentDefinition (element.getTagName(), context.extractSource(element))); RuntimeBeanReference pathMatcherRef = null ; if (element.hasAttribute("path-matcher" )) { pathMatcherRef = new RuntimeBeanReference (element.getAttribute("path-matcher" )); } List<Element> interceptors = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element, "bean" , "ref" , "interceptor" ); for (Element interceptor : interceptors) { RootBeanDefinition mappedInterceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition (MappedInterceptor.class); mappedInterceptorDef.setSource(context.extractSource(interceptor)); mappedInterceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); ManagedList<String> includePatterns = null ; ManagedList<String> excludePatterns = null ; Object interceptorBean; if ("interceptor" .equals(interceptor.getLocalName())) { includePatterns = getIncludePatterns(interceptor, "mapping" ); excludePatterns = getIncludePatterns(interceptor, "exclude-mapping" ); Element beanElem = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(interceptor, "bean" , "ref" ).get(0 ); interceptorBean = context.getDelegate().parsePropertySubElement(beanElem, null ); } else { interceptorBean = context.getDelegate().parsePropertySubElement(interceptor, null ); } mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(0 , includePatterns); mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(1 , excludePatterns); mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(2 , interceptorBean); if (pathMatcherRef != null ) { mappedInterceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("pathMatcher" , pathMatcherRef); } String beanName = context.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(mappedInterceptorDef); context.registerComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition (mappedInterceptorDef, beanName)); } context.popAndRegisterContainingComponent(); return null ; } private ManagedList<String> getIncludePatterns (Element interceptor, String elementName) { List<Element> paths = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(interceptor, elementName); ManagedList<String> patterns = new ManagedList <>(paths.size()); for (Element path : paths) { patterns.add(path.getAttribute("path" )); } return patterns; } }
逻辑不复杂,会将 <mvc:interceptor /> 标签解析 BeanDefinition 对象,beanClass 为 MappedInterceptor,解析出来的属性也会添加至其中,也就会给初始化成 MappedInterceptor 类型的 Spring Bean 到 Spring 上下文中
JavaConfig 在 SpringBoot 2.0+ 项目中,添加拦截器的方式可以如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Component public class JwtInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return true ; } @Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { } @Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { } } @Configuration public class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) { List<String> excludePath = new ArrayList <>(); registry.addInterceptor(jwtInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**" ).excludePathPatterns(excludePath); } @Bean public JwtInterceptor jwtInterceptor () { return new JwtInterceptor (); } }
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 接着来分析上面继承图中红色框部分的 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 系,该系是基于 Method 进行匹配。例如,我们所熟知的 @RequestMapping 等注解的方式。是通过AbstractHandlerMapping 的 getHandler 方法来获取的 ,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override @Nullable public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); return executionChain; }
在 AbstractHandlerMapping 获取 HandlerExecutionChain 处理器执行链的方法中,需要先调用 getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) 抽象方法,获取请求对应的处理器,该方法由子类去实现。 就上图中橙色框和红色框两类子类,本小节分析红色框部分内容。
注解相关 在SpringMVC体系的请求匹配注解如下:
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@Mapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@RequestMapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@GetMapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@PostMapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@PutMapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@DeleteMapping
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.@PatchMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping源码相关 org.springframework.web.servlet.result.method.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping,实现 InitializingBean 接口,继承 AbstractHandlerMapping 抽象类,以 Method 方法 作为 Handler 处理器 的 HandlerMapping 抽象类,提供 Mapping 的初始化、注册等通用的骨架方法。
构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping <T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { private boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = false ; @Nullable private HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy; private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry (); }
其中:
泛型,就是我们前面要一直提到的 Mapping 类型
mappingRegistry:Mapping 注册表,详细见下文
namingStrategy :org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy 接口,HandlerMethod 的 Mapping 的名字生成策略接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 @FunctionalInterface public interface HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy <T> { String getName (HandlerMethod handlerMethod, T mapping) ; } public class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy implements HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy <RequestMappingInfo> { public static final String SEPARATOR = "#" ; @Override public String getName (HandlerMethod handlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo mapping) { if (mapping.getName() != null ) { return mapping.getName(); } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); String simpleTypeName = handlerMethod.getBeanType().getSimpleName(); for (int i = 0 ; i < simpleTypeName.length(); i++) { if (Character.isUpperCase(simpleTypeName.charAt(i))) { sb.append(simpleTypeName.charAt(i)); } } sb.append(SEPARATOR).append(handlerMethod.getMethod().getName()); return sb.toString(); } }
情况一,如果 Mapping 已经配置名字,则直接返回 。例如,@RequestMapping(name = “login”, value = “user/login”) 注解的方法,它对应的 Mapping 的名字就是 login
情况二,如果 Mapping 未配置名字,则使用使用类名大写 + “#” + 方法名 。例如,@RequestMapping(value = “user/login”) 注解的方法,假设它所在的类为 UserController ,对应的方法名为 login ,则它对应的 Mapping 的名字就是 USERCONTROLLER#login
MappingRegistry 注册表 这个是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的内部类,Mapping 注册表
构造器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class MappingRegistry { private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap <>(); private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap <>(); private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap <>(); private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(); private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(); private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock (); }
其中:
registry :注册表。Key: Mapping,即 泛型;Value:MappingRegistration 对象(Mapping + HandlerMethod)
mappingLookup :注册表2。Key: Mapping,即 泛型;Value:HandlerMethod 对象
urlLookup :直接 URL 的映射。Key:直接 URL(就是固定死的路径,而非多个);Value:Mapping 数组
nameLookup :Mapping 的名字与 HandlerMethod 的映射。Key:Mapping 的名字;Value:HandlerMethod 数组
readWriteLock :读写锁,为了才操作上述属性时保证线程安全
register方法 register()方法,将 Mapping、Method、handler(方法所在类)之间的映射关系进行注册,会生成 HandlerMethod 对象 ,就是处理器对象,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public void register (T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { this .readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping); this .mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod); List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping); for (String url : directUrls) { this .urlLookup.add(url, mapping); } String name = null ; if (getNamingStrategy() != null ) { name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping); addMappingName(name, handlerMethod); } CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping); if (corsConfig != null ) { this .corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig); } this .registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration <>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name)); } finally { this .readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } }
其中:
获得写锁
添加相关映射至Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup属性
调用 createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) 方法,创建 HandlerMethod 对象,详情见下文
校验当前 Mapping 是否存在对应的 HandlerMethod 对象,如果已存在但不是前一步创建 HandlerMethod 对象则抛出异常,保证唯一性
将 Mapping 与 HandlerMethod 的映射关系保存至 mappingLookup
添加相关映射至MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup属性
调用 getDirectUrls 方法,获得 Mapping 对应的直接 URL 数组,如下:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private List<String> getDirectUrls (T mapping) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList <>(1 ); for (String path : getMappingPathPatterns(mapping)) { if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(path)) { urls.add(path); } } return urls; }
例如,@RequestMapping(“/user/login”) 注解对应的路径,就是直接路径
例如,@RequestMapping(“/user/${id}”) 注解对应的路径,不是直接路径,因为不确定性
将 url 和 Mapping 的映射关系保存至 urlLookup
添加相关映射至Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup属性
调用 HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy#getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, T mapping) 方法,获得 Mapping 的名字
调用 addMappingName(String name, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) 方法,添加 Mapping 的名字 + HandlerMethod 至 nameLookup ,如下:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private void addMappingName (String name, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) { List<HandlerMethod> oldList = this .nameLookup.get(name); if (oldList == null ) { oldList = Collections.emptyList(); } for (HandlerMethod current : oldList) { if (handlerMethod.equals(current)) { return ; } } List<HandlerMethod> newList = new ArrayList <>(oldList.size() + 1 ); newList.addAll(oldList); newList.add(handlerMethod); this .nameLookup.put(name, newList); }
初始化 CorsConfiguration 配置对象,TODO 暂时忽略
创建 MappingRegistration 对象,并和 Mapping 进行映射添加至 registry
释放写锁
unregister方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public void unregister (T mapping) {this .readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();try { MappingRegistration<T> definition = this .registry.remove(mapping); if (definition == null ) { return ; } this .mappingLookup.remove(definition.getMapping()); for (String url : definition.getDirectUrls()) { List<T> list = this .urlLookup.get(url); if (list != null ) { list.remove(definition.getMapping()); if (list.isEmpty()) { this .urlLookup.remove(url); } } } removeMappingName(definition); this .corsLookup.remove(definition.getHandlerMethod()); } finally { this .readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); }
和 register 方法逻辑相反,依次移除相关映射
createHandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method)方法,创建 Method 对应的 HandlerMethod 对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod (Object handler, Method method) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod; if (handler instanceof String) { String beanName = (String) handler; handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod (beanName, obtainApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory(), method); } else { handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod (handler, method); } return handlerMethod; }
其中:
如果 handler 类型为 String, 说明对应一个 Bean 对象的名称。例如 UserController 使用 @Controller 注解后,默认入参 handler 就是它的 beanName ,即 userController
如果 handler 类型非 String ,说明是一个已经是一个 handler 对象,就无需处理,直接创建 HandlerMethod 对象所以你会发现 HandlerMethod 处理器对象,就是handler(方法所在类)+method(方法对象)的组合,通过它能执行该方法
HandlerMethod 处理器 org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod,处理器对象,也就是某个方法的封装对象(Method+所在类的 Bean 对象),有以下属性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public class HandlerMethod { private final Object bean; @Nullable private final BeanFactory beanFactory; private final Class<?> beanType; private final Method method; private final Method bridgedMethod; private final MethodParameter[] parameters; @Nullable private HttpStatus responseStatus; @Nullable private String responseStatusReason; @Nullable private HandlerMethod resolvedFromHandlerMethod; @Nullable private volatile List<Annotation[][]> interfaceParameterAnnotations; }
它的构造函数非常多,不过原理都差不多,我们挑两个来看看
HandlerMethod(String beanName, BeanFactory beanFactory, Method method) 构造方法1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public HandlerMethod (String beanName, BeanFactory beanFactory, Method method) { Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name is required" ); Assert.notNull(beanFactory, "BeanFactory is required" ); Assert.notNull(method, "Method is required" ); this .bean = beanName; this .beanFactory = beanFactory; Class<?> beanType = beanFactory.getType(beanName); if (beanType == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Cannot resolve bean type for bean with name '" + beanName + "'" ); } this .beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanType); this .method = method; this .bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method); this .parameters = initMethodParameters(); evaluateResponseStatus(); }
HandlerMethod(Object bean, Method method) 构造方法1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public HandlerMethod (Object bean, Method method) { Assert.notNull(bean, "Bean is required" ); Assert.notNull(method, "Method is required" ); this .bean = bean; this .beanFactory = null ; this .beanType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(bean); this .method = method; this .bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method); this .parameters = initMethodParameters(); evaluateResponseStatus(); }
MappingRegistration 注册登记 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的私有静态内部类,Mapping 的注册登记信息,包含 Mapiing、HandlerMethod、直接 URL 路径、Mapping 名称,代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private static class MappingRegistration <T> { private final T mapping; private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod; private final List<String> directUrls; @Nullable private final String mappingName; public MappingRegistration (T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod, @Nullable List<String> directUrls, @Nullable String mappingName) { Assert.notNull(mapping, "Mapping must not be null" ); Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod must not be null" ); this .mapping = mapping; this .handlerMethod = handlerMethod; this .directUrls = (directUrls != null ? directUrls : Collections.emptyList()); this .mappingName = mappingName; } }
很简单,就是保存了 Mapping 注册时的一些信息
afterPropertiesSet 初始化方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public void afterPropertiesSet () { initHandlerMethods(); int total = this .getHandlerMethods().size(); if ((logger.isTraceEnabled() && total == 0 ) || (logger.isDebugEnabled() && total > 0 ) ) { logger.debug(total + " mappings in " + formatMappingName()); } } protected void initHandlerMethods () { String[] beanNames = obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class); for (String beanName : beanNames) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { Class<?> beanType = null ; try { beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'" , ex); } } if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }
detectHandlerMethods方法 detectHandlerMethods(Object handler)方法,初始化 Bean 下面的方法们为 HandlerMethod 对象,并注册到 MappingRegistry 注册表中,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 protected void detectHandlerMethods (final Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null ) { final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> getMappingForMethod(method, userType)); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods)); } methods.forEach((key, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(key, userType); registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } }
【重点】 getHandlerInternal方法 getHandlerInternal(ServerWebExchange exchange)方法,获得请求对应的 HandlerMethod 处理器对象,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); this .mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null ); } finally { this .mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
lookupHandlerMethod方法 lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) 获得请求对应的 HandlerMethod 处理器对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 @Nullable protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod (String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList <>(); List<T> directPathMatches = this .mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null ) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { addMatchingMappings(this .mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator (getMappingComparator(request)); matches.sort(comparator); Match bestMatch = matches.get(0 ); if (matches.size() > 1 ) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; } Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1 ); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0 ) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); throw new IllegalStateException ( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}" ); } } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(this .mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } }
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping,继承 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 抽象类,定义了使用的泛型 为 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo 类,即 Mapping 类型就是 RequestMappingInfo 对象
这样有什么好处呢? RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 定义了使用 RequestMappingInfo 对象,而其子类 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 将使用了 @RequestMapping 注解的方法,解析生成 RequestMappingInfo 对象。这样,如果未来我们自己定义注解,或者其他方式来生成 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 对象,未尝不可。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,实现 MatchableHandlerMapping、EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口,继承 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 抽象类,基于@RequestMapping 注解来构建 RequestMappingInfo 对象
构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping implements MatchableHandlerMapping , EmbeddedValueResolverAware { private boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = true ; private boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = false ; private boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = true ; private Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> pathPrefixes = new LinkedHashMap <>(); private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager = new ContentNegotiationManager (); @Nullable private StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver; private RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration config = new RequestMappingInfo .BuilderConfiguration(); }
afterPropertiesSet方法 因为父类 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,在 Sping 初始化该 Bean 的时候,会调用该方法,完成一些初始化工作 ,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet () { this .config = new RequestMappingInfo .BuilderConfiguration(); this .config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper()); this .config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher()); this .config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this .useSuffixPatternMatch); this .config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this .useTrailingSlashMatch); this .config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this .useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch); this .config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager()); super .afterPropertiesSet(); }
HandlerAdapter 组件 先来回顾一下在 DispatcherServlet 中处理请求的过程中哪里使用到 HandlerAdapter 组件,来看看DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch 方法中看看,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 protected void doDispatch (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null ; ModelAndView mv = null ; mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); } protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter (Object handler) throws ServletException { if (this .handlerAdapters != null ) { for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this .handlerAdapters) { if (adapter.supports(handler)) { return adapter; } } } throw new ServletException ("No adapter for handler [..." ); }
通过遍历 HandlerAdapter 组件们,判断是否支持处理该 handler 处理器,支持则返回该 HandlerAdapter 组件。所以获取处理器对应 HandlerAdapter 组件是有一定的先后顺序的,默认是HttpRequestHandlerAdapter -> SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter -> RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter 接口 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter接口,处理器的适配器,去执行处理器,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public interface HandlerAdapter { boolean supports (Object handler) ; @Nullable ModelAndView handle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception; long getLastModified (HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) ; }
初始化过程 在 DispatcherServlet 的 initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) 方法,会在 onRefresh 方法被调用,初始化 HandlerAdapter 组件,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private void initHandlerAdapters (ApplicationContext context) { this .handlerAdapters = null ; if (this .detectAllHandlerAdapters) { Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true , false ); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this .handlerAdapters = new ArrayList <>(matchingBeans.values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this .handlerAdapters); } } else { try { HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class); this .handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { } } if (this .handlerAdapters == null ) { this .handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerAdapters declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties" ); } } }
其中:
如果“开启”探测功能 ,则扫描已注册的 HandlerAdapter 的 Bean 们,添加到 handlerAdapters 中,默认开启,这里会进行排序,可以通过实现 Order 接口设置排序值如果“关闭”探测功能 ,则获得 Bean 名称为 “handlerAdapter” 对应的 Bean ,将其添加至 handlerAdapters如果未获得到,则获得默认配置的 HandlerAdapter 类 ,调用 getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class strategyInterface) 方法,就是从 DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中读取 HandlerAdapter 的默认实现类,如下: 1 2 3 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter =org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter、SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 三个实现类,接下来就一个一个分析
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,实现 HandlerAdapter 接口,基于 HttpRequestHandler 接口的 HandlerAdapter 实现类,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class HttpRequestHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports (Object handler) { return (handler instanceof HttpRequestHandler); } @Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response); return null ; } @Override public long getLastModified (HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L ; } } @FunctionalInterface public interface HttpRequestHandler { void handleRequest (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException; }
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports (Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Controller); } @Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); } @Override public long getLastModified (HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) { if (handler instanceof LastModified) { return ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request); } return -1L ; } } @FunctionalInterface public interface Controller { @Nullable ModelAndView handleRequest (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception; }
逻辑比较简单,和 HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 差不多,如果这个处理器实现了 Controoler 接口,则使用 HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 调用该处理器的 handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)方法去处理器请求,直接返回处理器执行后返回 ModelAndView。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,实现 BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean 接口,继承 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 抽象类,基于 @RequestMapping 注解的 HandlerMethod 处理器的 HandlerMethodAdapter 实现类
构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware , InitializingBean { public static final MethodFilter INIT_BINDER_METHODS = method -> AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, InitBinder.class); public static final MethodFilter MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS = method -> (!AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class) && AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, ModelAttribute.class)); @Nullable private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> customArgumentResolvers; @Nullable private HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite argumentResolvers; @Nullable private HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite initBinderArgumentResolvers; @Nullable private List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> customReturnValueHandlers; @Nullable private HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite returnValueHandlers; @Nullable private List<ModelAndViewResolver> modelAndViewResolvers; private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager = new ContentNegotiationManager (); private List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> messageConverters; private List<Object> requestResponseBodyAdvice = new ArrayList <>(); @Nullable private WebBindingInitializer webBindingInitializer; private AsyncTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor ("MvcAsync" ); @Nullable private Long asyncRequestTimeout; private CallableProcessingInterceptor[] callableInterceptors = new CallableProcessingInterceptor [0 ]; private DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor[] deferredResultInterceptors = new DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor [0 ]; private ReactiveAdapterRegistry reactiveAdapterRegistry = ReactiveAdapterRegistry.getSharedInstance(); private boolean ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect = false ; private int cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers = 0 ; private boolean synchronizeOnSession = false ; private SessionAttributeStore sessionAttributeStore = new DefaultSessionAttributeStore (); private ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer (); @Nullable private ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory; private final Map<Class<?>, SessionAttributesHandler> sessionAttributesHandlerCache = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(64 ); private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> initBinderCache = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(64 ); private final Map<ControllerAdviceBean, Set<Method>> initBinderAdviceCache = new LinkedHashMap <>(); private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> modelAttributeCache = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(64 ); private final Map<ControllerAdviceBean, Set<Method>> modelAttributeAdviceCache = new LinkedHashMap <>(); public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter () { StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter (); stringHttpMessageConverter.setWriteAcceptCharset(false ); this .messageConverters = new ArrayList <>(4 ); this .messageConverters.add(new ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter ()); this .messageConverters.add(stringHttpMessageConverter); try { this .messageConverters.add(new SourceHttpMessageConverter <>()); } catch (Error err) { } this .messageConverters.add(new AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter ()); } }
有许多的属性,不着急理解,先列几个主要的属性对象:
HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite argumentResolvers :参数处理器组合对象HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite returnValueHandlers :返回值处理器组合对象List messageConverters :HTTP 消息转换器集合对象List requestResponseBodyAdvice : RequestResponseAdvice 集合对象
在构造方法中默认会添加了四个 HttpMessageConverter 对象,当然,默认还会添加其他的,例如 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 为 JSON 消息格式的转换器
afterPropertiesSet 初始化方法 因为 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,在 Sping 初始化该 Bean 的时候,会调用该方法,完成一些初始化工作,方法如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet () { initControllerAdviceCache(); if (this .argumentResolvers == null ) { List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers(); this .argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite ().addResolvers(resolvers); } if (this .initBinderArgumentResolvers == null ) { List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers(); this .initBinderArgumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite ().addResolvers(resolvers); } if (this .returnValueHandlers == null ) { List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers(); this .returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite ().addHandlers(handlers); } }
initControllerAdviceCache 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 private void initControllerAdviceCache () { if (getApplicationContext() == null ) { return ; } List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans); List<Object> requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans = new ArrayList <>(); for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) { Class<?> beanType = adviceBean.getBeanType(); if (beanType == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Unresolvable type for ControllerAdviceBean: " + adviceBean); } Set<Method> attrMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS); if (!attrMethods.isEmpty()) { this .modelAttributeAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, attrMethods); } Set<Method> binderMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, INIT_BINDER_METHODS); if (!binderMethods.isEmpty()) { this .initBinderAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, binderMethods); } if (RequestBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType) || ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) { requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(adviceBean); } } if (!requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.isEmpty()) { this .requestResponseBodyAdvice.addAll(0 , requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { int modelSize = this .modelAttributeAdviceCache.size(); int binderSize = this .initBinderAdviceCache.size(); int reqCount = getBodyAdviceCount(RequestBodyAdvice.class); int resCount = getBodyAdviceCount(ResponseBodyAdvice.class); if (modelSize == 0 && binderSize == 0 && reqCount == 0 && resCount == 0 ) { logger.debug("ControllerAdvice beans: none" ); } else { logger.debug("ControllerAdvice beans: " + modelSize + " @ModelAttribute, " + binderSize + " @InitBinder, " + reqCount + " RequestBodyAdvice, " + resCount + " ResponseBodyAdvice" ); } } }
其中:
从 Spring 上下文扫描 @ControllerAdvice 注解的 Bean 们,生成对应的 ControllerAdviceBean 对象,并将进行排序,方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans (ApplicationContext context) { return Arrays.stream(BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context, Object.class)) .filter(name -> !ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(name)) .filter(name -> context.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class) != null ) .map(name -> new ControllerAdviceBean (name, context)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); }
@ControllerAdvice 注解:用于 Controller 类的增强类,其中可定义多种增强的方法,例如 @ExceptionHandler 注解的方法用于处理器 Controller 抛出的异常
遍历 1 中生成 ControllerAdviceBean 数组
扫描有 @ModelAttribute ,无 @RequestMapping 注解的方法,添加到 modelAttributeAdviceCache 属性中,该类方法用于在执行方法前修改 Model 对象
扫描有 @InitBinder 注解的方法,添加到 initBinderAdviceCache 属性中,该类方法用于在执行方法前初始化数据绑定器
如果是 RequestBodyAdvice 或 ResponseBodyAdvice 的子类,保存至 requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans 临时变量中
将 2.3 的 requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans 保存至 requestResponseBodyAdvice 属性中
getDefaultArgumentResolvers方法 初始化默认的参数解析器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> getDefaultArgumentResolvers () { List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = new ArrayList <>(); resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory(), false )); resolvers.add(new RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor (false )); resolvers.add(new RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor (getMessageConverters(), this .requestResponseBodyAdvice)); resolvers.add(new RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver (getMessageConverters(), this .requestResponseBodyAdvice)); resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory())); resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory())); resolvers.add(new ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory())); resolvers.add(new SessionAttributeMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new RequestAttributeMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new HttpEntityMethodProcessor (getMessageConverters(), this .requestResponseBodyAdvice)); resolvers.add(new RedirectAttributesMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ModelMethodProcessor ()); resolvers.add(new MapMethodProcessor ()); resolvers.add(new ErrorsMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new SessionStatusMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver ()); if (getCustomArgumentResolvers() != null ) { resolvers.addAll(getCustomArgumentResolvers()); } resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory(), true )); resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor (true )); return resolvers; }
getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers 初始化默认的参数绑定器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers () { List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = new ArrayList <>(); resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory(), false )); resolvers.add(new RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory())); resolvers.add(new SessionAttributeMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new RequestAttributeMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver ()); resolvers.add(new ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver ()); if (getCustomArgumentResolvers() != null ) { resolvers.addAll(getCustomArgumentResolvers()); } resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver (getBeanFactory(), true )); return resolvers; }
getDefaultReturnValueHandlers 初始化默认的返回值处理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 private List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> getDefaultReturnValueHandlers () { List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = new ArrayList <>(); handlers.add(new ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new ModelMethodProcessor ()); handlers.add(new ViewMethodReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new ResponseBodyEmitterReturnValueHandler (getMessageConverters(), this .reactiveAdapterRegistry, this .taskExecutor, this .contentNegotiationManager)); handlers.add(new StreamingResponseBodyReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new HttpEntityMethodProcessor (getMessageConverters(), this .contentNegotiationManager, this .requestResponseBodyAdvice)); handlers.add(new HttpHeadersReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new CallableMethodReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new AsyncTaskMethodReturnValueHandler (this .beanFactory)); handlers.add(new ModelAttributeMethodProcessor (false )); handlers.add(new RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor (getMessageConverters(), this .contentNegotiationManager, this .requestResponseBodyAdvice)); handlers.add(new ViewNameMethodReturnValueHandler ()); handlers.add(new MapMethodProcessor ()); if (getCustomReturnValueHandlers() != null ) { handlers.addAll(getCustomReturnValueHandlers()); } if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(getModelAndViewResolvers())) { handlers.add(new ModelAndViewResolverMethodReturnValueHandler (getModelAndViewResolvers())); } else { handlers.add(new ModelAttributeMethodProcessor (true )); } return handlers; }
【重点】 invokeHandlerMethod方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 @Nullable protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest (request, response); try { WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod); if (this .argumentResolvers != null ) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this .argumentResolvers); } if (this .returnValueHandlers != null ) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this .returnValueHandlers); } invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory); invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this .parameterNameDiscoverer); ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer (); mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this .ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this .asyncRequestTimeout); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this .taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this .callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this .deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0 ]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> { String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn); return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]" ; }); invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null ; } return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } finally { webRequest.requestCompleted(); } }
因为,Spring MVC 提供了大量的特性,所以 HandlerAdapter 又涉及许多组件。😈我们的目的是,看到怎么调用 HandlerMethod 方法的,即调用 Controller 的 @RequestMapping 注解的方法。
创建 ServletWebRequest 对象,包含了 request 请求和 response响应
调用 getDataBinderFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) 方法,创建 WebDataBinderFactory 对象,有关于数据绑定,暂时忽略
调用 getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) 方法,创建 ModelFactory 对象,有关于往 Model 对象设置数据,暂时忽略
【核心】 调用 createInvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) 方法,创建 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 对象,然后设置其属性。本文会对 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 做简单的解析。
创建 ModelAndViewContainer 对象,并初始其相关属性
创建 AsyncWebRequest 异步请求对象,暂时忽略
创建 WebAsyncManager 异步请求管理器对象,暂时忽略
异步处理,并发结果相关,暂时忽略
【核心】 调用 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 的invokeAndHandle()方法,执行处理器,方法如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 public void invokeAndHandle (ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs); setResponseStatus(webRequest); if (returnValue == null ) { if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) { disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest); mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true ); return ; } } else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) { mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true ); return ; } mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false ); Assert.state(this .returnValueHandlers != null , "No return value handlers" ); try { this .returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex); } throw ex; } } @Nullable public Object invokeForRequest (NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args)); } return doInvoke(args); } @Nullable protected Object doInvoke (Object... args) throws Exception { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod()); try { return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { assertTargetBean(getBridgedMethod(), getBean(), args); String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument" ); throw new IllegalStateException (formatInvokeError(text, args), ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException(); if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) targetException; } else if (targetException instanceof Error) { throw (Error) targetException; } else if (targetException instanceof Exception) { throw (Exception) targetException; } else { throw new IllegalStateException (formatInvokeError("Invocation failure" , args), targetException); } } }
异步处理,并发结果相关,暂时忽略
调用 getModelAndView() 方法,获得 ModelAndView 对象,方法如下:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Nullable private ModelAndView getModelAndView (ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception { modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer); if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) { return null ; } ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel(); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView (mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus()); if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) { mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView()); } if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) { Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes(); HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class); if (request != null ) { RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes); } } return mav; }
情况一,如果 mavContainer 已处理,则返回“空”的 ModelAndView 对象,@ResponseBody 注解的结果处理则直接返回 null
情况二,如果 mavContainer 未处理,则基于 mavContainer 生成 ModelAndView 对象
标记请求完成,暂时忽略
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod HandlerMethodArgumentResolver HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler HttpMessageConverter HttpMessageConverter 组件。在 HandlerAdapter 执行处理器的过程中,具体的执行过程交由 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 对象来完成,
在使用 Spring MVC 时,@RequestBody 和 @ResponseBody 两个注解,分别完成请求报文到 Java 对象、Java 对象到响应报文的转换,底层的实现就是通过 Spring 3.x 中引入的 HttpMessageConverter 消息转换机制来实现的。
先来理解一些概念,在处理 HTTP 请求的过程中,需要解析请求体,返回结果设置到响应体。在 Servlet 标准中,javax.servlet.ServletRequest 和 javax.servlet.ServletResponse 分别有有以下方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 public ServletInputStream getInputStream () throws IOException;public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream () throws IOException;
通过上面两个方法可以获取到请求体和响应体,ServletInputStream 和 ServletOutputStream 分别继承 java 中的 InputStream 和 OutputStream 流对象,可以通过它们获取请求报文和设置响应报文。再通过 HttpMessageConverter 消息转换机制来解析请求报文或者设置响应报文。
HandlerExceptionResolver组件 RequestToViewNameTranslator 组件 LocaleResolver 组件 ViewResolver 组件